Difference between revisions of "1620 Geographos"
(1998 KY26) Tag: Removed redirect |
(→Geographos in Orbiter: Added content.) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {| cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" style="margin:25px 0 0 10px; border:3px solid lightsteelblue;width:250px; font-size: | + | {| cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" style="margin:25px 0 0 10px; border:3px solid lightsteelblue;width:250px; font-size:90%; font-family:'Arial','Helvetica'; float: right; clear: right;"Template in Orbiter" |
| − | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2" align="center" | | + | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2" align="center" |1620 Geographos |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" align="center"|[[Image: | + | |colspan="2" align="center"|[[Image:1620 Geographos.png|240px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" align="center"|''' | + | |colspan="2" align="center"|'''Geographos in Orbiter''' |
|- | |- | ||
!bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Designation | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Designation | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Name||align="right"| | + | |Name||align="right"|1620 Geographos |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Reference body||align="right"|Sun | + | |width="30%"|Reference body||align="right" width="30%"|Sun |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Number of satellites||align="right" width="30%"|0 | + | |width="30%"|Number of satellites||align="right" width="30%"|0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Planetary mean | + | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Planetary mean orbits |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Epoch||align="right"|2006 | + | |width="30%"|Epoch||align="right" width="50%"|2006 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Semimajor axis (a)||align="right" | | + | |width="30%"|Semimajor axis (a)||align="right" width="50%"| 186315638173 km<br>(1.24544311568598 AU) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Eccentricity (e)||align="right"|0. | + | |width="30%"|Eccentricity (e)||align="right" width="30%"| 0.335415102834536 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Inclination (i)||align="right"| | + | |width="30%"|Inclination (i)||align="right" width="30%"|0.232845464045468 radian<br>(13.3410623685705°) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |width="30%"|Longitude of the ascending node (LAN, ☊)||align="right" width="30%"|5.88689533166951 radian<br>337.29425693993° | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Longitude of | + | |width="30%"|Longitude of periapsis (ϖ)||align="right" width="30%"|10.7178284350264 radian<br>614.086334872317° |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |width="30%"|Mean longitude (L)||align="right" width="30%"|12.5060362286656 radian<br>716.543094340244° |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Rotational Elements | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |width="30%"|Sidereal Rotation Period||align="right" width="50%"|18802.8 seconds<br>(5.223 hours) | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |width="30%"|Sidereal Rotation Offset||align="right" width="50%"|0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |width="30%"|Obliquity||align="right" width="30%"|0.1 radians<br>0° |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
!bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Selected physical parameters | !bgcolor="lightsteelblue" colspan="2"|Selected physical parameters | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |width="30%"|Mean radius||align="right" | + | |width="30%"|Mean radius||align="right" width="30%"| 3450 m |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |width="30%"|Mass||align="right" width="30%"|4×10<su>12</sup> kg |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |width="30%"|Equatorial gravity||align="right" width="30%"|0.000022 m/s<sup>2</sup> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |width="30%"|Escape velocity||align="right" width="30%"| 0.0004 m/s | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |width="30%"|Gravity at surface||aligh="right" width="30%"|Geographos 1%<br>Sun 99% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |width="30%"|Note||align="right" width="30%"|*Elements given are from Geographos.cfg file. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 87: | Line 59: | ||
|4=All versions | |4=All versions | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1620 Geographos''' is a Near-Earth object discovered in 1951 by [[w:Albert George Wilson|Albert George Wilson]] and [[w:Rudolph Minkowski]] at [[w:Palomar Observatory|Palomar]] and is named in honor of the [[w:National Geographic Society]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Geographos was to be visited by the [[w:Clementine mission]], failed to reach the body. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Geographos in Orbiter == | ||
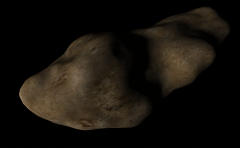
| + | 1620 Geographos was modeled in Orbiter as a somewhat potato shaped object about 5 km on the longest dimension. Because the visual surface of Geographos is well below the hard radius of the body, landing anywhere on the body's radius you end up well above the visual surface. Because even at the surface, geographos only provides 1% of the local gravity, the [[Sun]] providing the other 99%, a ship cannot orbit Geographos, it can only fly along with it in solar orbit, maneuvering in its vicinity. A ship also cannot land and remain on the hard surface, it will immediately drift off the surface. When maneuvering in the vicinity, have SurfaceMFD up so that the pilot can monitor the ship's altitude above the surface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Gallery == | ||
| + | <gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | ||
| + | Animation_of_1620_Geographos_orbit.gif|Animation of the orbit of Geographos as compared to [[Venus]], [[Earth]] and [[Mars]] from 2010 to 2020.<br>From Wikimedia Commons. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{SolarSystem}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Articles|Geographos]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Celestial bodies|Geographos]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Solar System|Geographos]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Near-Earth objects|Geographos]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:24, 27 May 2024
|
Project home: Asteroid Pack 1.00 |
1620 Geographos is a Near-Earth object discovered in 1951 by Albert George Wilson and w:Rudolph Minkowski at Palomar and is named in honor of the w:National Geographic Society.
Geographos was to be visited by the w:Clementine mission, failed to reach the body.
Geographos in Orbiter[edit]
1620 Geographos was modeled in Orbiter as a somewhat potato shaped object about 5 km on the longest dimension. Because the visual surface of Geographos is well below the hard radius of the body, landing anywhere on the body's radius you end up well above the visual surface. Because even at the surface, geographos only provides 1% of the local gravity, the Sun providing the other 99%, a ship cannot orbit Geographos, it can only fly along with it in solar orbit, maneuvering in its vicinity. A ship also cannot land and remain on the hard surface, it will immediately drift off the surface. When maneuvering in the vicinity, have SurfaceMFD up so that the pilot can monitor the ship's altitude above the surface.
Gallery[edit]
| edit The Solar System | |
|---|---|
| Central star |
Sun (Sol) |
| Planets |
Mercury - Venus - Earth - Mars - Jupiter - Saturn - Uranus - Neptune |
| Natural satellites |
Moon - Phobos - Deimos - Io - Europa - Ganymede - Titan - more... |
| Add-ons |
Planets - Dwarf Planets - Small objects - Natural satellites - Alternative star systems |