Orbit MFD
Orbit is an MFD mode which lists the elements and parameters for the orbit of the ship's orbit in reference to a central body, and a graphical representation of the orbit. The mode can also show the orbit of a target body orbiting the same body and its orbital characteristics. Orbit may be selected from the MFD selection page.
The display shows the Keplar, or two-body, orbit of the craft at the current date with respect to the reference body. Any natural body in Orbiter may be selected as the reference body. Because of perturbations to the orbit, it may change over time. Perturbing effects include other bodies in the Solar System, nonspherical gravity, atmospheric drag, and ship's engines, etc.
The orbital elements may be displayed in the ecliptic or equatorial frame of reference. The plane of the ecliptic is the orbital plane of the Earth and the equatorial plane is the plane of the equator of the reference body. ShiftF or the FRM button is used to switch back and forth between the reference frames, the 'Frm' value displays the current frame.
The graphical view can be switched between the planes of the ecliptic (ECL), equator (EQU), ship's orbit (SHP), or target's orbit (TGT) with ShiftP or with the PRJ button. The radius vector of the ship and target can be displayed from orbit focus (indicated by Rad, ApR, PeR), or by altitude above mean planet radius (Alt, ApA, PeA) with ShiftD, or the DST button.
ShiftT or the TGT button opens a popup menu to select a target object, if you want no target, use ShiftN or the NT button. You can only display orbits for targets orbiting the selected reference object can be displayed.
Press ShiftH or the HUD button to switch the HUD to display the orbit reference object.
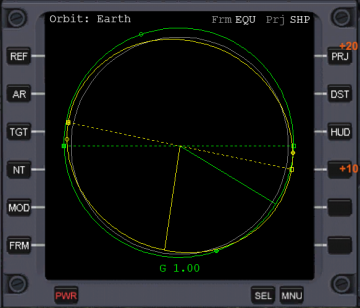
In the graphic mode:
•The gray circle represents the mean radius of the reference object (Sun, planet, or moon).
•The green circle, ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola represents the Kepler orbit of your ship.
•The yellow circle, ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola represents the Kepler orbit of the target.
•The small open circle on the ship's or target's orbit represents the apoapsis of the orbit.
•The small closed circle on the ship's or target's orbit represents the periapsis of the orbit.
•The line from the center of the body to the orbit is the radius vector, the end of the line where it touches the orbit is the ship's or body's current location.
•The dotted line represents the line of nodes of the target orbit and your ship's orbit.
•The filled in square at one end of the line of nodes represents the ascending node of your orbit.
•The open square at the other end of the line of nodes represents the descending node of your orbit.
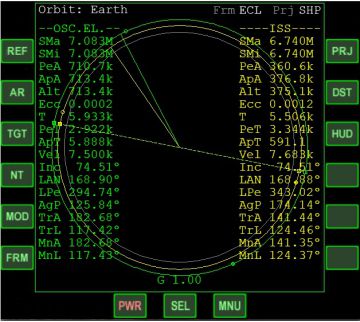
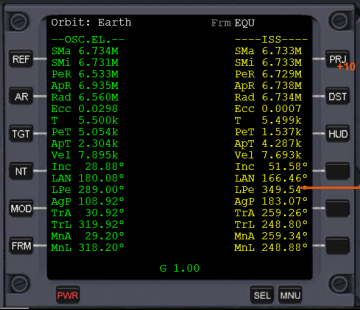
In the list mode:
•Orbit: indicates the body about which the ship and/or the target is orbiting.
•Frm indicates the frame of reference, Equator (ECL) or Ecliptic (ECL)
•G represents the percentage of gravity exerted by the reference body (0-1.00). If the G value is less than 0.8, it will turn yellow, and less than 0.5 it will turn red. ShiftA will change the reference body to the dominant one.
•--OSC.EL.-- indicates that the list for your ship lists the osculating elements of your orbit.
•SMa indicates the semimajor axis of the orbit
•SMi indicates the semiminor axis of the orbit
•PeR (when selected by the DST button) indicates the periapsis of the orbit from the center of the body.
•PeA (when selected by the DST button) indicates the periapsis of the orbit from the mean radius of the body.
•ApR (when selected by the DST button) indicates the apoapsis of the orbit from the center of the body.
•ApA (when selected by the DST button) indicates the apoapsis of the orbit from the mean radius of the body.
•Rad (when selected by the DST button) indicates the current radius of the ship or target from the center of the body.
•Alt (when selected by the DST button) indicates the altitude ot the ship or target from the mean radius of the body.
•Ecc indicates the eccentricity of the orbit (0 = circular, >0 and <1 elliptical, 1 = parabolic, >1 Hyperbolic).
•T indicates the orbital period in seconds (how long it takes to make one orbit).
•PeT indicates the time in seconds until the ship or target passes the next periapsis.
•ApT indicates time in seconds until the ship or target passes the next apoapsis.
•Vel current velocity of the ship or target in meters per second.
•Inc inclination of the orbit in degrees (<180° indicates a prograde orbit, >180° indicates a retrograde orbit).
•LAN indicates Longitude of the Ascending Node or the angle in degrees between the ship's or target's position to the ascending node.
•LPe indicates Longitude of Periapsis or the angle in degrees from the vernal equinox to the periapsis of the ship's or target's orbit.
•AgP indicates the argument of periapsis or the angle in degrees from the ascending node to the periapsis of the ship's or target's orbit.
•TrA indicates the true anomaly, or the angle in degrees from the periapsis of the orbit to the ship's or target's current position.
•TrL indicates the true longitude or the angle in degrees from the vernal equinox to the ship or target's position if the inclination of the orbit were zero.
•MnA indicates the mean anomaly of the orbit or the angle from the vernal equinox to the ship's position if the orbit was circular, the ship or target moved at constant speed, and having the same orbital period as the true orbit.
•MnL indicates the mean longitude of the orbit or the angle from the vernal equinox to the ship's or target's position if it's orbit was circular and with no perterbations.
See also[edit]
- Orbit at Wikipedia.